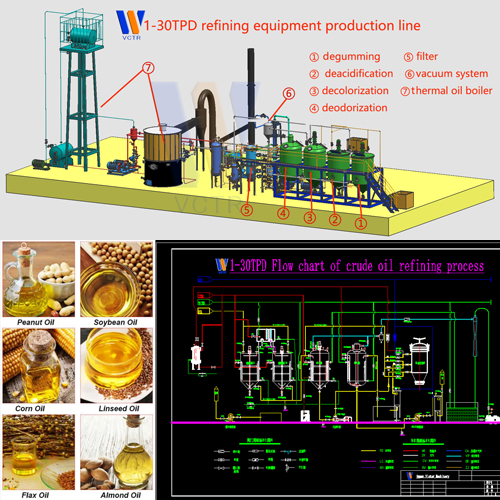
Oil refining-Bleaching
1. The purpose of bleaching
All kinds of oils have different colors because they contain different pigments. For example, chlorophyll makes oils dark green; carotene makes oils yellow; during storage, sugars and proteins decompose to make oils brown; gossypol makes cottonseed oil dark brown.
In the mentioned refining method, although part of the pigment in the oil can be removed at the same time, it cannot reach a satisfactory level. Therefore, for the production of high-end oils-salad oil, cosmetic oil, light-colored paint, light-colored soap and margarine, the color should be light. Only the refining method mentioned above can not meet the requirements, and it must be bleaching.
2. Bleaching method
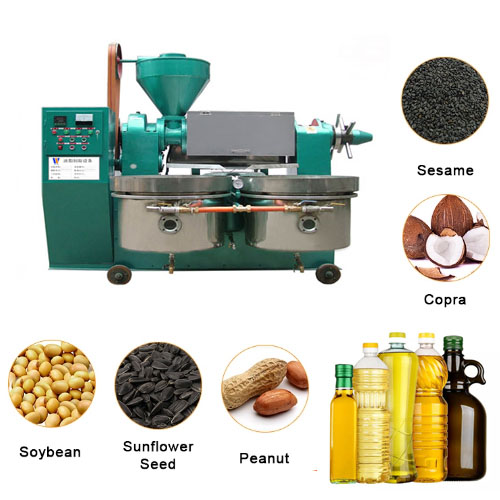
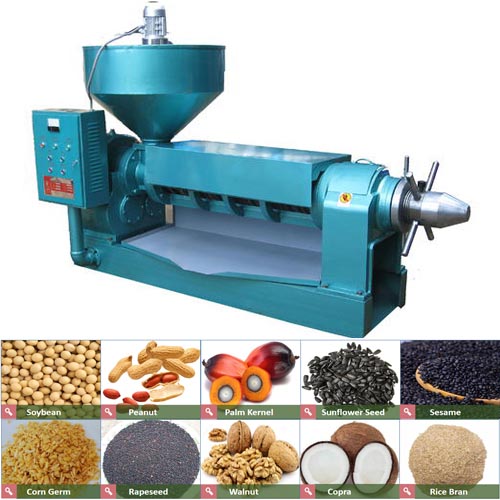
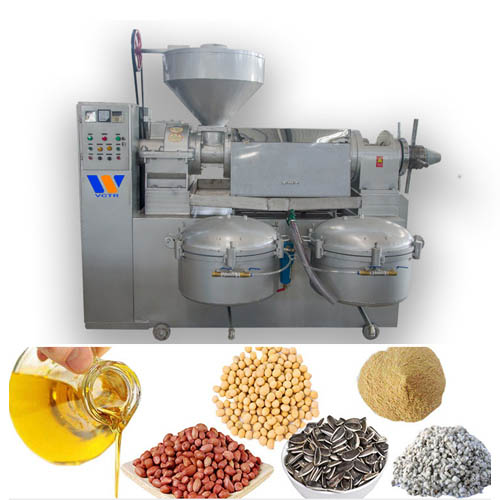
The bleaching method of oil include sunlight bleaching method (also known as oxidation method), chemical bleaching method, heating method and adsorption method. At present, the most widely used method is the adsorption method, which is to add some substances with strong adsorption capacity (acid activated clay, bleaching earth, activated carbon, etc.) to oil, and absorb and remove the pigment and other impurities (protein, mucus, Resin and soap etc.).
3. Process flow
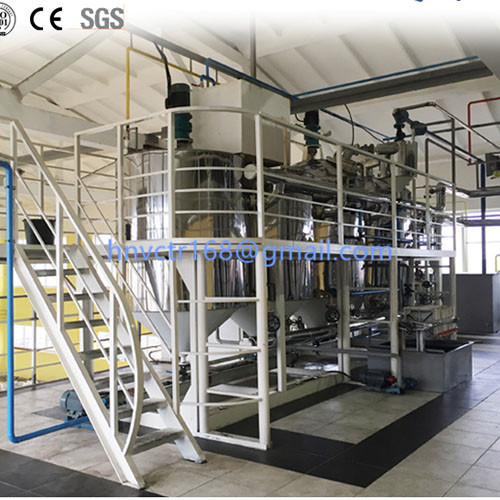
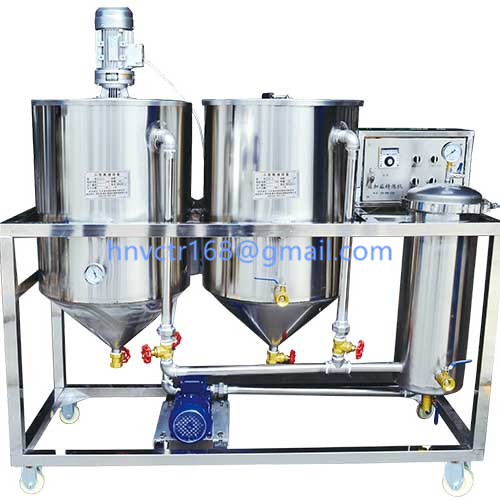
Bacth bleaching is a process in which oil and adsorbents complete the bleaching process through a single adsorption equilibrium under bacth conditions.
The bleached oil is transferred to the bleaching tank through the storage tank, and after heating and drying under vacuum, it fully contacts with the adsorbent sucked in from the adsorbent tank under stirring to complete the adsorption balance, and then the adsorbent is separated by the oil pump and the filter press after cooling. After filtering, the bleached oil enters the storage tank and transfers to the bleaching process by means of vacuum suction or oil transfer pump. The adsorbent filter cake in the filter press is transferred to the treatment tank and the residual oil is collected.
4. Adsorption bleaching process parameters
①Quality requirements for deacidified oil
Production of advanced cooking oil:
Water and volatile matter: ≤0.2%;
Impurities: ≤0.2%;
Soap content: ≤100 mg/kg;
Acid value (calculated in KOH): ≤0.4 mg/g;
Color (Lovibond 25.4mm): Y50R3.
Production of salad oil:
Water and volatile matter: ≤0.2%;
Impurities: ≤0.2%;
Soap content: ≤100 mg/kg;
Acid value (calculated in KOH): ≤0.2 mg/g;
Color (Lovibond 25.4mm): Y50R3.
②Consumption index:
Cooling water volume (20℃, 0.3MPa): 3.5m3/ton;
Electricity: (380 volts, 2206.5 watts, 50 Hz) 7 kilowatts·hour/ton;
Steam (1 MPa): 120 kg/ton;
Oil content of waste bleaching earth: <35%.
③Health protection
Workshop hygiene:
The maximum allowable concentration of dust in the clay feeding room is 10 mg/m3;
Exhaust emissions:
The maximum allowable dust concentration of the gas discharged from the clay conveying system to the outdoors is 150 mg/m3.
Hot tags:Bleaching,Bleaching method,Adsorption bleaching,bleaching earth,Consumption index
All kinds of oils have different colors because they contain different pigments. For example, chlorophyll makes oils dark green; carotene makes oils yellow; during storage, sugars and proteins decompose to make oils brown; gossypol makes cottonseed oil dark brown.
In the mentioned refining method, although part of the pigment in the oil can be removed at the same time, it cannot reach a satisfactory level. Therefore, for the production of high-end oils-salad oil, cosmetic oil, light-colored paint, light-colored soap and margarine, the color should be light. Only the refining method mentioned above can not meet the requirements, and it must be bleaching.
2. Bleaching method
The bleaching method of oil include sunlight bleaching method (also known as oxidation method), chemical bleaching method, heating method and adsorption method. At present, the most widely used method is the adsorption method, which is to add some substances with strong adsorption capacity (acid activated clay, bleaching earth, activated carbon, etc.) to oil, and absorb and remove the pigment and other impurities (protein, mucus, Resin and soap etc.).
3. Process flow
Bacth bleaching is a process in which oil and adsorbents complete the bleaching process through a single adsorption equilibrium under bacth conditions.
The bleached oil is transferred to the bleaching tank through the storage tank, and after heating and drying under vacuum, it fully contacts with the adsorbent sucked in from the adsorbent tank under stirring to complete the adsorption balance, and then the adsorbent is separated by the oil pump and the filter press after cooling. After filtering, the bleached oil enters the storage tank and transfers to the bleaching process by means of vacuum suction or oil transfer pump. The adsorbent filter cake in the filter press is transferred to the treatment tank and the residual oil is collected.
4. Adsorption bleaching process parameters
①Quality requirements for deacidified oil
Production of advanced cooking oil:
Water and volatile matter: ≤0.2%;
Impurities: ≤0.2%;
Soap content: ≤100 mg/kg;
Acid value (calculated in KOH): ≤0.4 mg/g;
Color (Lovibond 25.4mm): Y50R3.
Production of salad oil:
Water and volatile matter: ≤0.2%;
Impurities: ≤0.2%;
Soap content: ≤100 mg/kg;
Acid value (calculated in KOH): ≤0.2 mg/g;
Color (Lovibond 25.4mm): Y50R3.
②Consumption index:
Cooling water volume (20℃, 0.3MPa): 3.5m3/ton;
Electricity: (380 volts, 2206.5 watts, 50 Hz) 7 kilowatts·hour/ton;
Steam (1 MPa): 120 kg/ton;
Oil content of waste bleaching earth: <35%.
③Health protection
Workshop hygiene:
The maximum allowable concentration of dust in the clay feeding room is 10 mg/m3;
Exhaust emissions:
The maximum allowable dust concentration of the gas discharged from the clay conveying system to the outdoors is 150 mg/m3.
Hot tags:Bleaching,Bleaching method,Adsorption bleaching,bleaching earth,Consumption index