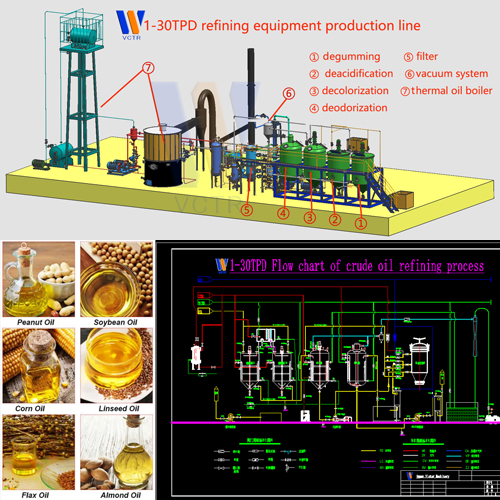
What are the bleaching agents used for vegetable oil refining and bleaching?
The bleaching of edible oil is part of the oil refining process. At present, the most widely used bleaching agent in the oil refining and bleaching industry is activated bleaching earth. In addition, there are are other bleaching agents such as activated carbon,attapulgite,natural bleaching earth,zeolite,diatomaceous earth,and other bleaching agents.
Our country is rich in bentonite resources and is the world's largest producer of bentonite. The annual consumption of bentonite in our country is about 5 million tons, of which 40% is used in the iron ore pellet market, 30% is used in the foundry market, and activated bleaching earth accounts for about 10%.Mainly used for the edible oil refining and bleaching and purification of petroleum, grease, paraffin, wax oil, kerosene and other minerals in the petroleum industry.There are also applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
1. Activated bleaching earth
The annual demand for activated bleaching earth for oil refining and bleaching is about 200,000 tons. In 2016, our country's consumption of edible oils and fats reached a record 30 million tons. The demand for bleaching agents is increasing year by year, but there are many manufacturers of activated bleaching earth and the quality is uneven. in addition, because the price of activated bleaching earth is higher than that of attapulgite, the current application of activated bleaching earth in the oil refining and bleaching industry not only has fierce competition within the industry, but also always faces challenges from other bleaching materials such as attapulgite.
2. Activated carbon
Activated carbon is made by carbonization of sawdust, bagasse, chaff, hard nut shell, etc., and then chemically or physically activated. Its main component-carbon content is as high as 90-98%, density is 1.9-2.1 tons/M3, bulk density is 0.08-0.45 tons/M3, has loose pores, large specific surface area, high bleaching coefficient, and hydrophobicity. It can absorb high-molecular substances and is particularly effective in removing blue and green pigments. It can also remove the flash of oil brought by trace mineral oil. In addition, it has strong adsorption capacity for gases, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and pesticide residues. Due to its high price and high oil absorption rate, it is often used together with bleaching earth or activated bleaching earth in the oil bleaching operation. The mixing ratio is usually 1:10-20. Mixed use can significantly improve the bleaching ability, and can remove the smell of bleached oil.
3. Attapulgite
Attapulgite is a magnesium-rich fibrous mineral whose main component is silicon dioxide. This kind of clay is delicate and has a bluish gray or off-white appearance. Farmers in the producing area used it as a feed additive and no animal disease was found. Attapulgite has a good bleaching effect. Compared with activated bleaching earth, the amount of bleaching is less, the oil loss is small, and the price is low. The problem is that it is difficult to filter, so the fineness of the clay should be increased appropriately.
4. Natural bleaching earth
Natural bleaching earth, scientific name bentonite. Its main component is (Al4Si8O20(OH)4•nH2O), with a small amount of Ca, Mg,Fe, Na, K and other components. The pH of the suspension is 5-6, which is acidic, so it is also called acid clay.
Natural bleaching earth is processed only by physical methods from mining to final grinding and classification. Its structure is microporous crystal or amorphous, and its specific surface area is much larger than that of other clays. It has certain activity, but its bleaching coefficient is low (referring to the same batch of grease before and after bleaching, while observing the ratio of oil column height when the same color is reached) , The oil absorption rate is also high, so it is gradually replaced by activated bleaching earth.
5. Zeolite
Zeolite is a multi-cycle and multi-mineral lake basin deposit between acidic volcanic lava and clastic deposits.Many series of volcanic glass are melted or hydrolyzed to form clinoptilolite deposits, which are obtained by mining, screening, grinding, and sieving zeolite adsorbent.Its chemical composition is mainly silica, followed by alumina.Zeolite has a good bleaching effect. It can also reduce the acid value and moisture of the oil when decolorizing. The price is cheaper than activated clay. It is a new material for oil bleaching.
6. Diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth is evolved from the remains of single-celled potassium silicate shells under the action of natural forces. Diatomaceous earth with good purity is white, generally light gray or light reddish brown. The main chemical component is silicon dioxide. It has a certain adsorption capacity for pigments, but the bleaching coefficient is low and the oil absorption rate is high. It is in the oil industry production used as a filter aid.
7. Other decolorizing agents
The adsorbents used in oil bleaching include activated alumina and alumina treated with sulfurous acid.
Our country is rich in bentonite resources and is the world's largest producer of bentonite. The annual consumption of bentonite in our country is about 5 million tons, of which 40% is used in the iron ore pellet market, 30% is used in the foundry market, and activated bleaching earth accounts for about 10%.Mainly used for the edible oil refining and bleaching and purification of petroleum, grease, paraffin, wax oil, kerosene and other minerals in the petroleum industry.There are also applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
1. Activated bleaching earth
The annual demand for activated bleaching earth for oil refining and bleaching is about 200,000 tons. In 2016, our country's consumption of edible oils and fats reached a record 30 million tons. The demand for bleaching agents is increasing year by year, but there are many manufacturers of activated bleaching earth and the quality is uneven. in addition, because the price of activated bleaching earth is higher than that of attapulgite, the current application of activated bleaching earth in the oil refining and bleaching industry not only has fierce competition within the industry, but also always faces challenges from other bleaching materials such as attapulgite.
2. Activated carbon
Activated carbon is made by carbonization of sawdust, bagasse, chaff, hard nut shell, etc., and then chemically or physically activated. Its main component-carbon content is as high as 90-98%, density is 1.9-2.1 tons/M3, bulk density is 0.08-0.45 tons/M3, has loose pores, large specific surface area, high bleaching coefficient, and hydrophobicity. It can absorb high-molecular substances and is particularly effective in removing blue and green pigments. It can also remove the flash of oil brought by trace mineral oil. In addition, it has strong adsorption capacity for gases, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and pesticide residues. Due to its high price and high oil absorption rate, it is often used together with bleaching earth or activated bleaching earth in the oil bleaching operation. The mixing ratio is usually 1:10-20. Mixed use can significantly improve the bleaching ability, and can remove the smell of bleached oil.
3. Attapulgite
Attapulgite is a magnesium-rich fibrous mineral whose main component is silicon dioxide. This kind of clay is delicate and has a bluish gray or off-white appearance. Farmers in the producing area used it as a feed additive and no animal disease was found. Attapulgite has a good bleaching effect. Compared with activated bleaching earth, the amount of bleaching is less, the oil loss is small, and the price is low. The problem is that it is difficult to filter, so the fineness of the clay should be increased appropriately.
4. Natural bleaching earth
Natural bleaching earth, scientific name bentonite. Its main component is (Al4Si8O20(OH)4•nH2O), with a small amount of Ca, Mg,Fe, Na, K and other components. The pH of the suspension is 5-6, which is acidic, so it is also called acid clay.
Natural bleaching earth is processed only by physical methods from mining to final grinding and classification. Its structure is microporous crystal or amorphous, and its specific surface area is much larger than that of other clays. It has certain activity, but its bleaching coefficient is low (referring to the same batch of grease before and after bleaching, while observing the ratio of oil column height when the same color is reached) , The oil absorption rate is also high, so it is gradually replaced by activated bleaching earth.
5. Zeolite
Zeolite is a multi-cycle and multi-mineral lake basin deposit between acidic volcanic lava and clastic deposits.Many series of volcanic glass are melted or hydrolyzed to form clinoptilolite deposits, which are obtained by mining, screening, grinding, and sieving zeolite adsorbent.Its chemical composition is mainly silica, followed by alumina.Zeolite has a good bleaching effect. It can also reduce the acid value and moisture of the oil when decolorizing. The price is cheaper than activated clay. It is a new material for oil bleaching.
6. Diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth is evolved from the remains of single-celled potassium silicate shells under the action of natural forces. Diatomaceous earth with good purity is white, generally light gray or light reddish brown. The main chemical component is silicon dioxide. It has a certain adsorption capacity for pigments, but the bleaching coefficient is low and the oil absorption rate is high. It is in the oil industry production used as a filter aid.
7. Other decolorizing agents
The adsorbents used in oil bleaching include activated alumina and alumina treated with sulfurous acid.